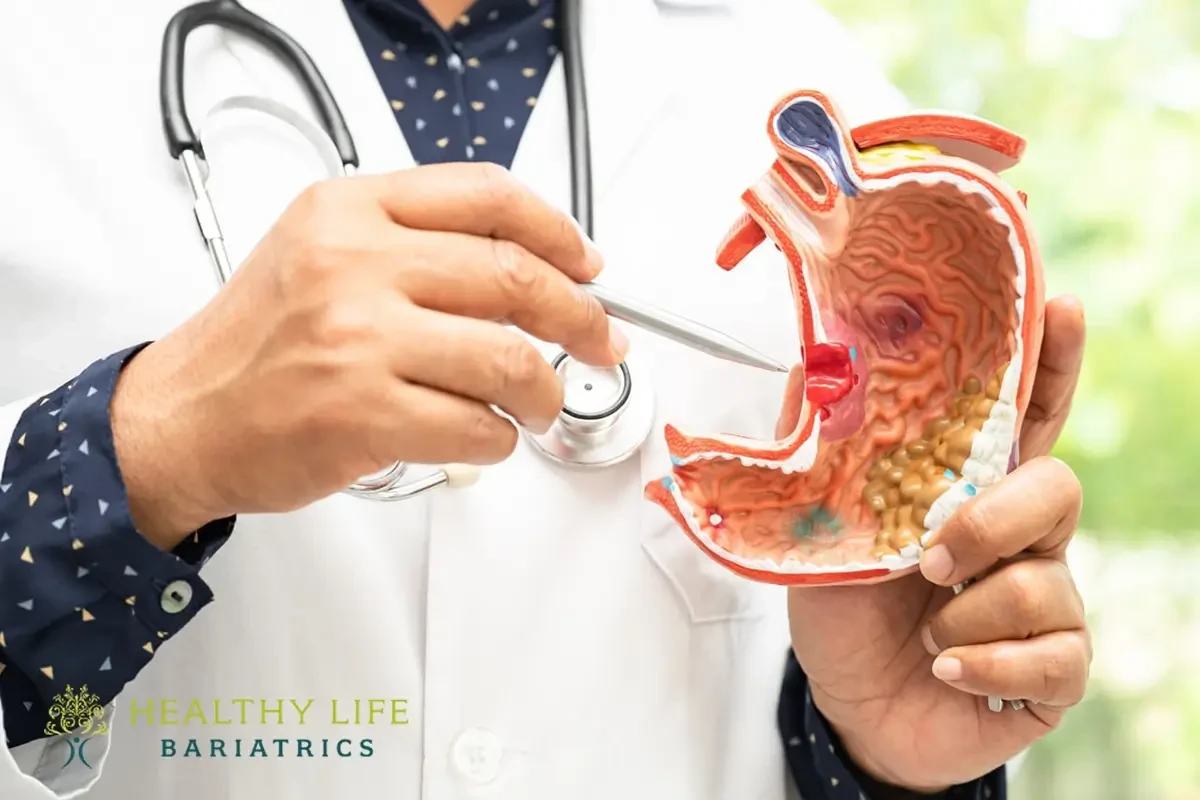
After gastric sleeve surgery, it is important to avoid certain medications, particularly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen, as well as prescription NSAIDs like diclofenac and celecoxib. These medications can increase the risk of stomach irritation, ulcers, and gastrointestinal bleeding, which can be particularly harmful after gastric sleeve surgery when the stomach is more sensitive.
Instead, it is recommended to use acetaminophen for pain relief, as it is less likely to cause these complications. Your doctor may also prescribe alternative pain medications that are safe to use after gastric sleeve surgery.
The timeframe for when it may be safe to take NSAIDs again can vary for each patient and should be discussed with your healthcare provider. Generally, it is advisable to avoid NSAIDs for at least 3 to 6 months after surgery to allow for proper healing of the stomach. However, this timeframe may differ based on individual circumstances, so it is crucial to seek personalized medical advice.
In summary, it is important to avoid NSAIDs and prescription NSAIDs after gastric sleeve surgery to minimize the potential risks of stomach irritation, ulcers, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Always consult with your doctor before resuming the use of these medications.